Do you know the names of planets and things found in space? Let’s find out what the different types of planets and things are found in space. The video is made for kids and does not contain any details. I have added links to NASA and other sites below each image because I presume this article is helpful not only for kids but also for other science students studying in higher classes.
Names Of Planets For Kids
Solar System

Our solar system consists of our star, the Sun, and everything bound to it by gravity – the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune; dwarf planets such as Pluto; dozens of moons; and millions of asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. Explore Our Solar System in Depth
Names Of Planets In Our Solar System
Click on the thumbnail to view full-size image
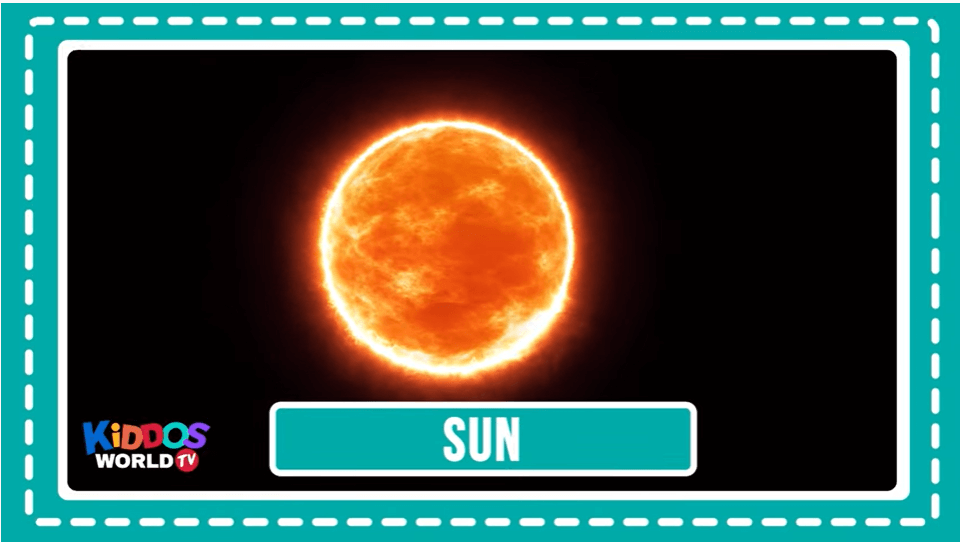
The Sun is a star. There are lots of stars in the universe, but the Sun is the closest one to Earth, and it’s the only one in our solar system. It is the center of our solar system.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About the Sun
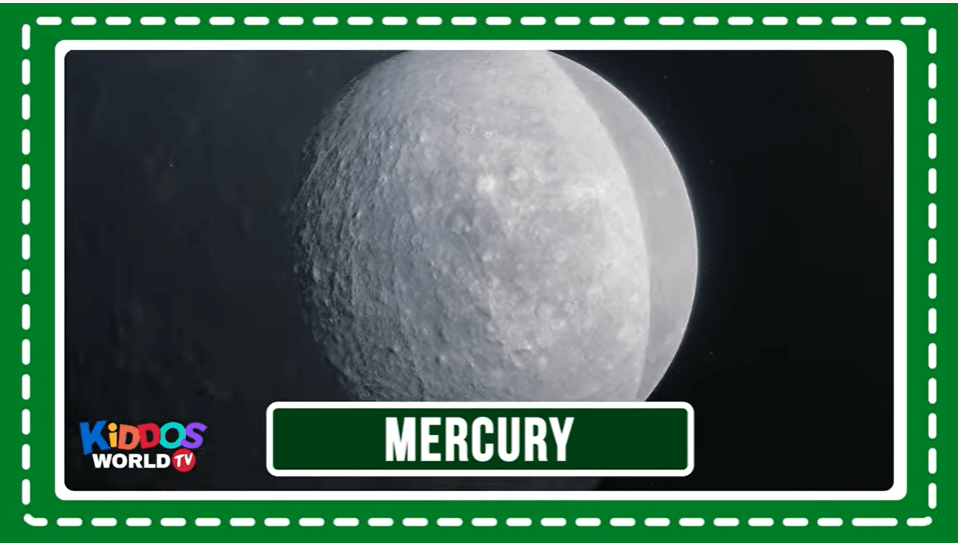
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system. It’s a little bigger than Earth’s Moon. It is the closest planet to the Sun, but it’s actually not the hottest. Venus is hotter.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Mercury

Venus is the second planet from the Sun and Earth’s closest planetary neighbor. Even though Mercury is closer to the Sun, Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Venus

Our home planet Earth is a rocky, terrestrial planet. It has a solid and active surface with mountains, valleys, canyons, plains and so much more. Earth is special because it is an ocean planet. Water covers 70% of Earth’s surface.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Earth
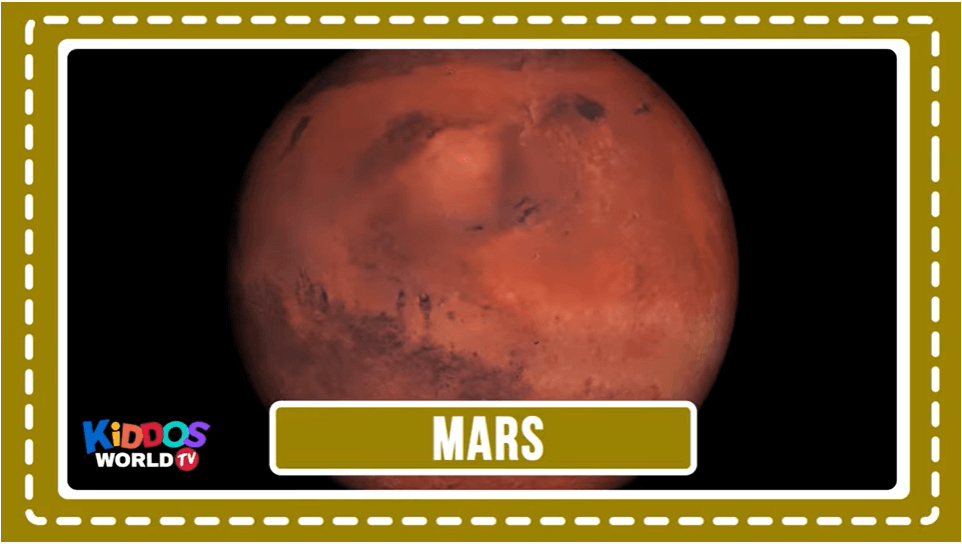
Mars is a cold desert world. It is half the size of Earth. Mars is sometimes called the Red Planet. It’s red because of rusty iron in the ground. Like Earth, Mars has seasons, polar ice caps, volcanoes, canyons, and weather.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Mars

Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system. It’s similar to a star, but it never got big enough to start burning. Jupiter is covered in swirling cloud stripes. It has big storms like the Great Red Spot, which has been going for hundreds of years.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Jupiter

Saturn isn’t the only planet to have rings, but it definitely has the most beautiful ones. The rings we see are made of groups of tiny ringlets that surround Saturn. They’re made of chunks of ice and rock.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Saturn

Uranus is made of water, methane, and ammonia fluids above a small rocky center. Its atmosphere is made of hydrogen and helium like Jupiter and Saturn, but it also has methane. The methane makes Uranus blue.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Uranus

Neptune is dark, cold, and very windy. It’s the last of the planets in our solar system. It’s more than 30 times as far from the Sun as Earth is. Neptune is very similar to Uranus. Neptune has six rings, but they’re very hard to see.
Visit NASA Space Place for more kid-friendly facts. NASA Space Place: All About Neptune

Space shuttle, also called Space Transportation System, partially reusable rocket-launched vehicle designed to go into orbit around Earth, to transport people and cargo to and from orbiting spacecraft, and to glide to a runway landing on its return to Earth’s surface. Britannica
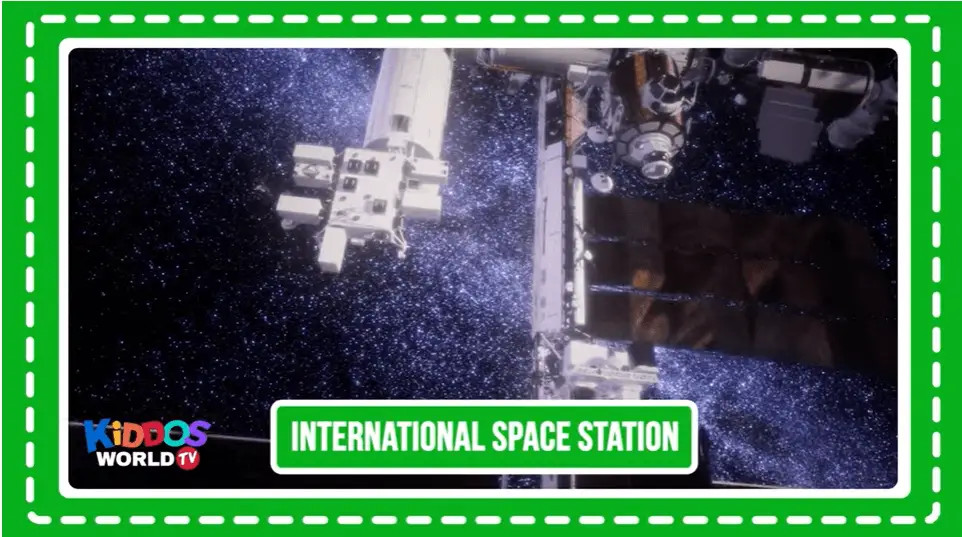
The International Space Station (ISS) is a multi-nation construction project that is the largest single structure humans ever put into space. Its main construction was completed between 1998 and 2011, although the station continually evolves to include new missions and experiments. Space

A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying. NASA Black Hole

A nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas in space. Some nebulae (more than one nebula) come from the gas and dust thrown out by the explosion of a dying star, such as a supernova. Other nebulae are regions where new stars are beginning to form. NASA Nebula

The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy’s appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. Wikipedia

A satellite is an object in space that orbits or circles around a bigger object. There are two kinds of satellites: natural (such as the moon orbiting the Earth) or artificial (such as the International Space Station orbiting the Earth). Space

astronaut, a designation, derived from the Greek words for “star” and “sailor,” commonly applied to an individual who has flown in outer space. More specifically, in the West, astronaut refers to those from the United States, Canada, Europe, and Japan who travel into space. Britannica

A rover is a planetary surface exploration device designed to move across the solid surface on a planet or other planetary mass celestial bodies. Some rovers have been designed as land vehicles to transport members of a human spaceflight crew; others have been partially or fully autonomous robots. Wikipedia

The Lunar Module (LM) – originally called the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM) and still pronounced “lem” after the name was changed – was the spacecraft that allowed the Apollo astronauts to land on the Moon. Space Foundation

Asteroids, sometimes called minor planets, are rocky, airless remnants left over from the early formation of our solar system about 4.6 billion years ago. Explore Asteroids In Depth
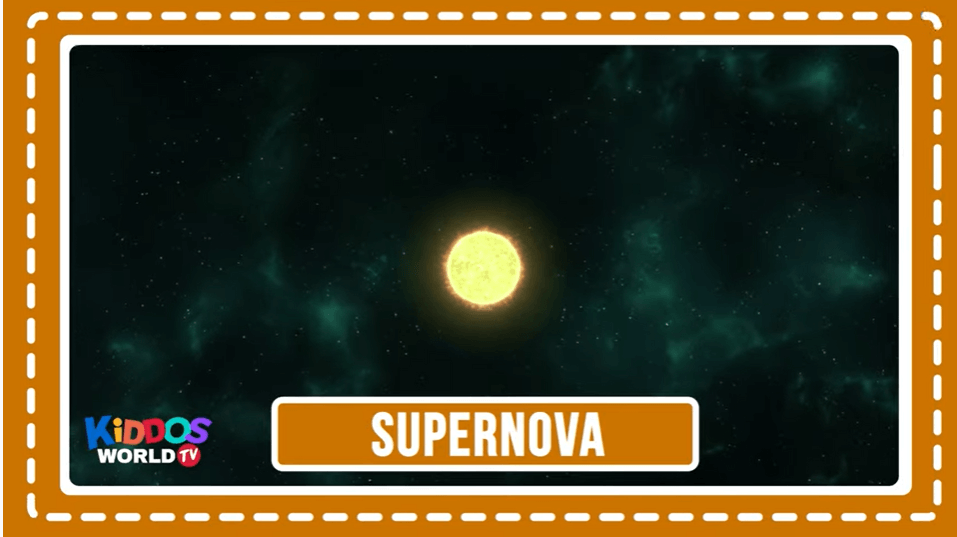
A supernova is the biggest explosion that humans have ever seen. Each blast is the extremely bright, super-powerful explosion of a star. NASA Science Supernova
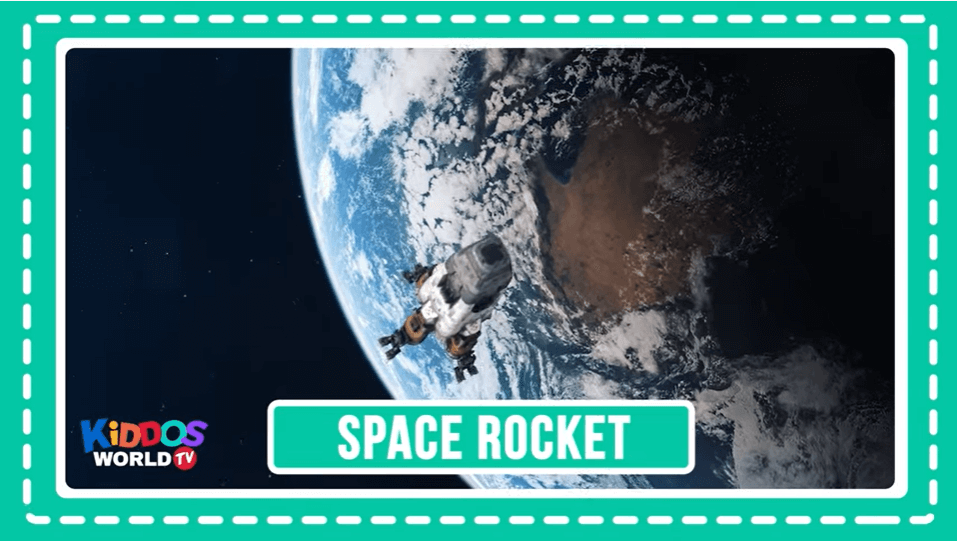
We launch satellites and spacecraft into space by putting them on rockets carrying tons of propellants. The propellants give the rocket enough energy to boost away from Earth’s surface. NASA Science Space Rocket

Comets are frozen leftovers from the formation of the solar system composed of dust, rock, and ices. They range from a few miles to tens of miles wide, but as they orbit closer to the Sun, they heat up and spew gases and dust into a glowing head that can be larger than a planet. This material forms a tail that stretches millions of miles. Explore Comets in Depth

The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite and the fifth largest moon in the solar system. The brightest and largest object in our night sky, the Moon makes Earth a more livable planet by moderating our home planet’s wobble on its axis, leading to a relatively stable climate. Explore Earth’s Moon In Depth

Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is typical: it has hundreds of billions of stars, enough gas and dust to make billions more stars, and at least ten times as much dark matter as all the stars and gas put together. And it’s all held together by gravity. NASA Science Galaxy
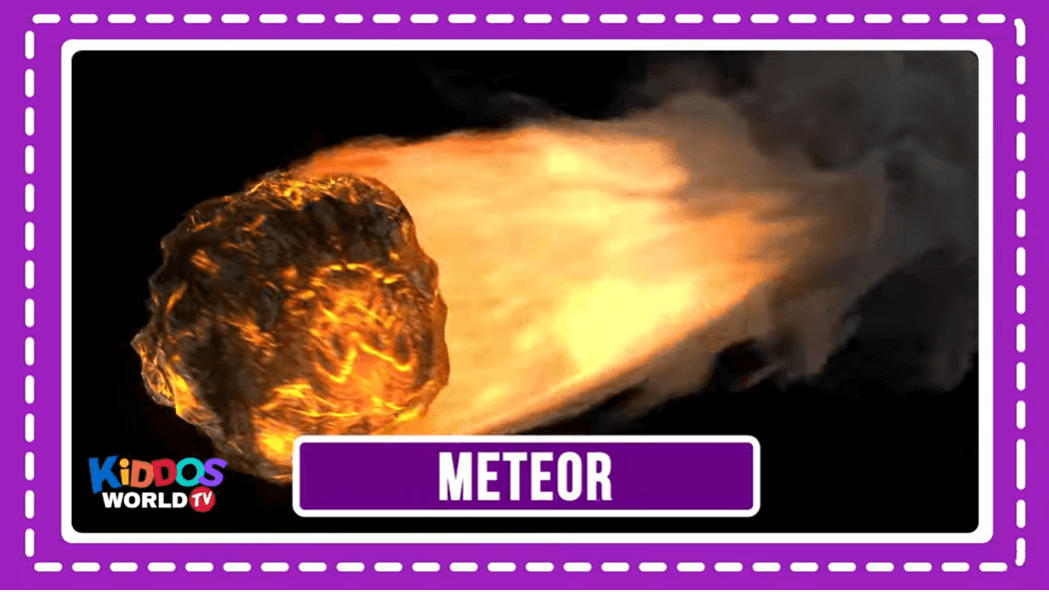
When meteoroids enter Earth’s atmosphere (or that of another planet, like Mars) at high speed and burn up, the fireballs or “shooting stars” are called meteors. Explore Meteors and Meteorites In Depth

Neutron stars are formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses. The very central region of the star – the core – collapses, crushing together every proton and electron into a neutron. NASA Neutron stars

The spacecraft lander is a protective “shell” that houses the rover and protects it, along with the airbags, from the forces of impact. NASA Lander

Stars are the most widely recognized astronomical objects, and represent the most fundamental building blocks of galaxies. The age, distribution, and composition of the stars in a galaxy trace the history, dynamics, and evolution of that galaxy. NASA Stars

White dwarfs are what is left when stars like our sun have exhausted all of their fuel. They are dense, dim, stellar corpses — the last observable stage of evolution for low- and medium-mass stars. Space
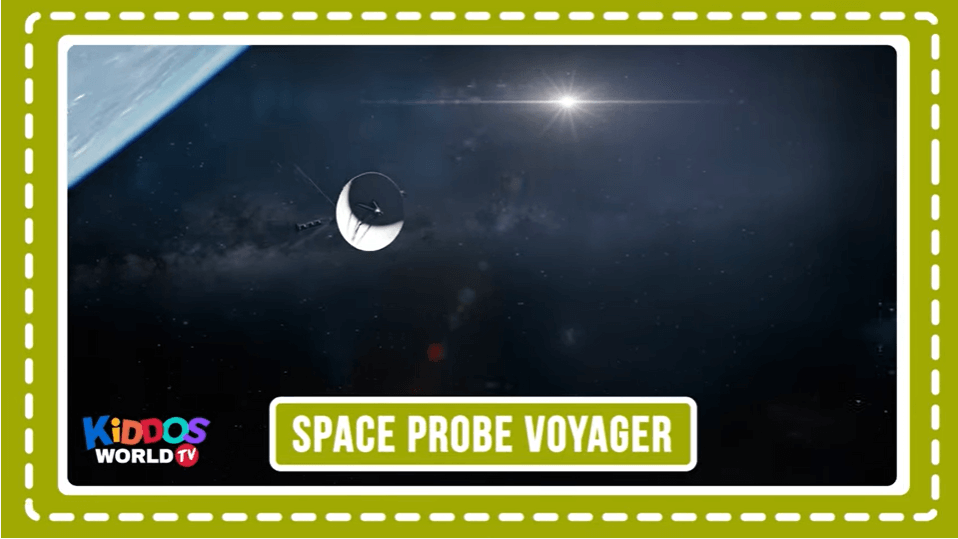
Voyager, in space exploration, either of a pair of robotic U.S. interplanetary probes launched to observe and to transmit information to Earth about the giant planets of the outer solar system and the farthest reaches of the Sun’s sphere of influence. Britannica
Dwarf

Pluto is a dwarf planet that lies in the Kuiper Belt, an area full of icy bodies and other dwarf planets out past Neptune. Pluto is very small, only about half the width of the United States and its biggest moon Charon is about half the size of Pluto. NASA Space Place: All About Pluto

Dwarf planet Ceres is the largest object in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, and it’s the only dwarf planet located in the inner solar system. Ceres is named for the Roman goddess of corn and harvests. The word cereal comes from the same name. NASA Ceres Dwarf Planet

Slightly smaller than Pluto, Makemake is the second-brightest object in the Kuiper Belt as seen from Earth (while Pluto is the brightest). It takes about 305 Earth years for this dwarf planet to make one trip around the Sun. NASA Makemake Dwarf Planet

Haumea is roughly the same size as Pluto. It is one of the fastest rotating large objects in our solar system. The fast spin distorts Haumea’s shape, making this dwarf planet look like a football. NASA Haumea Dwarf Planet

Eris is one of the largest known dwarf planets in our solar system. It’s about the same size as Pluto but is three times farther from the Sun. At first, Eris appeared to be larger than Pluto. NASA Eris Dwarf Planet
Final Thoughts
Hope you found the above information about the names of planets and things found in space useful. Some links from NASA are specially for Kids and other links are useful for students studying in higher classes. Links for kids to NASA space place are good because those pages contain many useful and fun activities, questions and answers and creative work. Kids can learn many things about the names of planets in depth.
Top 60 Famous Landmarks In The World For Kids’ Learning
Thank you for your visit.
Don’t forget to share it.
Leave your thoughts in the comment box below.

Mathukutty P. V. is the founder of Simply Life Tips. He is a Blogger, Content Writer, Influencer, and YouTuber. He is passionate about learning new skills. He is the Director of PokketCFO.
He lives with the notion of “SIMPLE LIVING, CREATIVE THINKING”. He Believes – “Sharing is caring.” and “Learning never ends.”



